Author: Sun WuKong
-
Recent research has uncovered fascinating details about a set of exquisite and practical medical instruments utilized by Roman surgeons approximately 2,000 years ago. A team from the University of Exeter in the UK employed advanced scanning technology to study six surgical artifacts, which comprise a bronze scalpel handle, two surgical probes, two needles, and a…
-
Thoth, the Egyptian deity revered for wisdom, writing, and knowledge, occupies a prominent place in ancient mythology. Whether you are a student of history, a lover of myths, or simply inquisitive about past civilizations, exploring Thoth’s significance can enhance your comprehension of the cultural and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egyptians. Who is Thoth in Ancient…
-
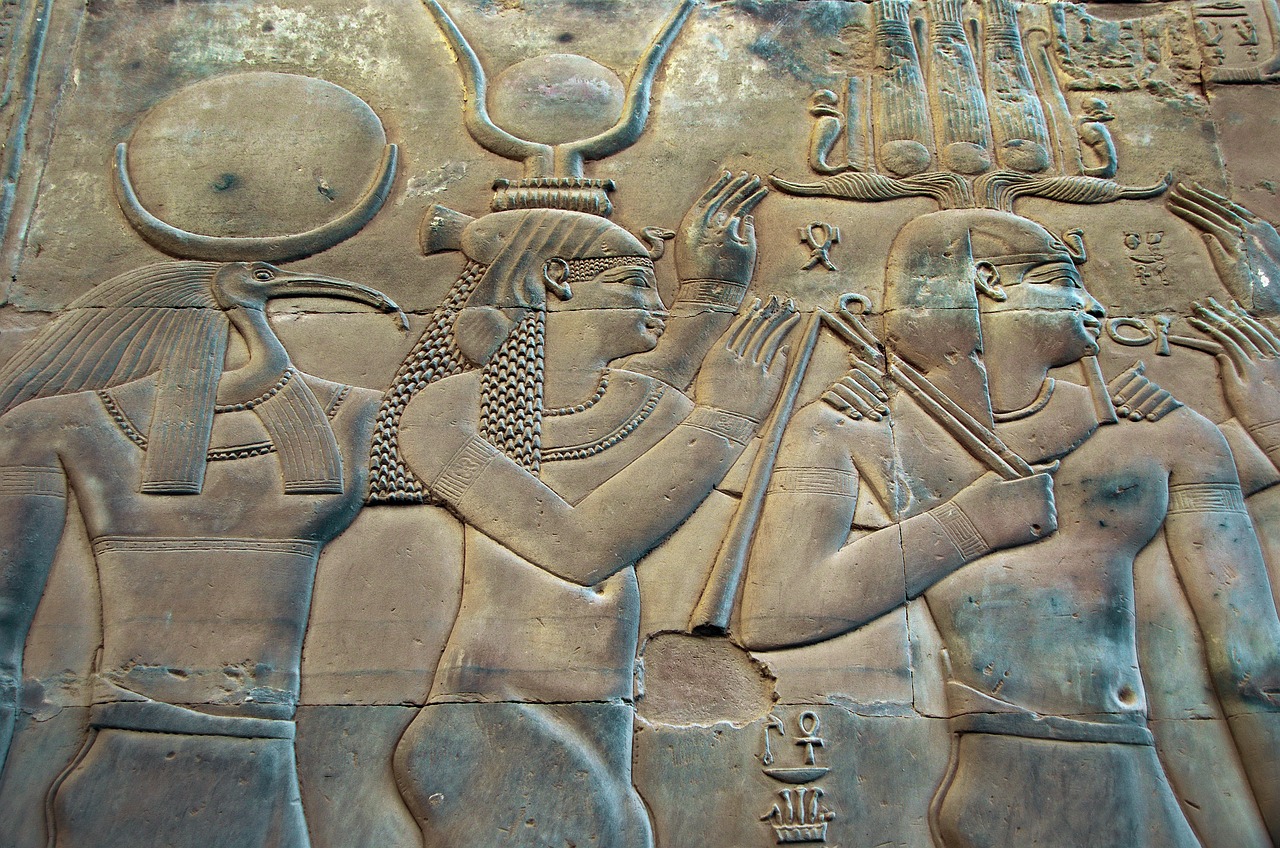
Ancient Egyptian religion refers to the spiritual beliefs and practices that were part of the societal framework of ancient Egypt, dating back to as early as the 4th millennium BCE and continuing until the decline of traditional culture in the first centuries CE. Understanding these religious paradigms requires contextualizing them within the extensive history of…
-
Discovering the Magic of Dukkah: A Flavorful Egyptian Blend Straight from the heart of Egypt, I’m excited to share with you the art of making dukkah—an alluring mix of nuts, seeds, and spices that’s both fragrant and delicious. This quick-to-prepare recipe can be kept on hand for various uses such as a savory snack with…
-
Erebus, in ancient Greek mythology, represents the deity associated with a shadowy domain of the underworld and serves as the embodiment of darkness itself. This primordial figure is traced back to the Greek creation narrative, where he is recognized as a descendant of Chaos, which also is the origin of his spouse, Nyx, the embodiment…
-
The Story of Chiron: The Wise Centaur In the epic “Iliad,” Homer refers to Chiron as the most knowledgeable and fair of all centaurs. His tale begins with a tragic background, tied to the cruel fate of his father Cronus, the Titan god, who consumed each of his offspring at birth to prevent being overthrown.…
-
Exploring the Distinct Identities of Heket and Hekate Since becoming a Heketean in 2008, I have encountered the tendency to conflate Heket and Hekate early in my studies, which has long puzzled me. While their similarities in etymology are evident, I felt that any suggested parallels were largely superficial. After creating a brief analysis on…
-
Geb: The Earth God in Ancient Egyptian Mythology In the intriguing realm of ancient mythology, every civilization boasts its own set of deities, divinely tasked with governing various facets of existence and the cosmos. Within the ancient Egyptian belief system, Geb emerged as the powerful deity presiding over the Earth. The Roots of Geb Referred…
-
Roman religion encompasses the beliefs, practices, and rituals practiced by the inhabitants of the Italian Peninsula from prehistoric times until the rise of Christianity in the 4th century CE, a period referred to as Classical antiquity. Cicero, the prominent orator and politician, asserted that the Romans excelled others due to their distinctive wisdom, acknowledging that…
-
The Significance and Evolution of Christian Faith Why is faith, known as pistis or fides in the classical languages, vital to Christians? What does it signify, and how was it practiced within early Christian communities? Are the concepts of Christian faith fundamentally different from the divine-human pistis/fides found in Greek, Roman religions, or ancient Judaism,…