Roman Mythology
-
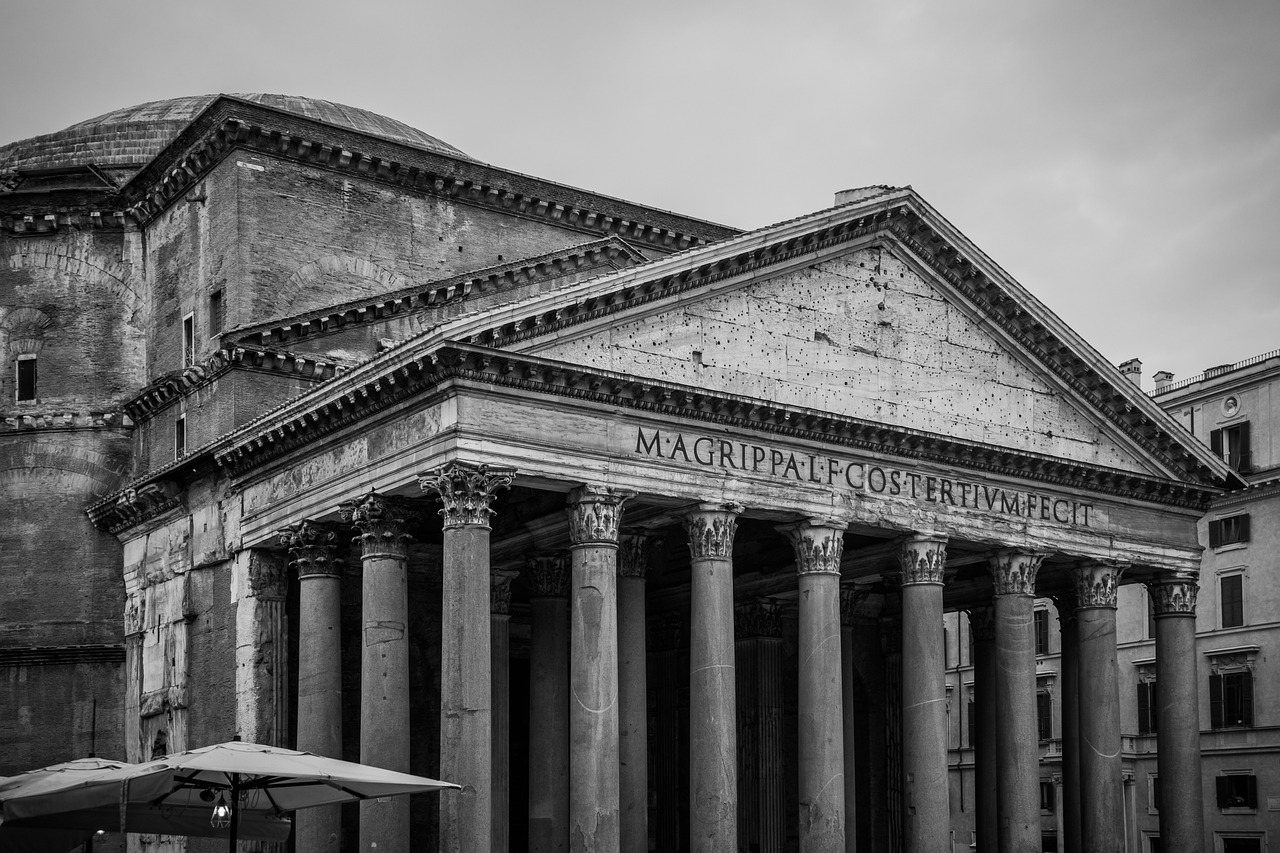

The Pantheon in Rome, an architectural marvel, traces its origins back to 27 BC when Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa initiated the construction of what appears to have been a typical Classical temple—a rectangular structure featuring a gabled roof and a surrounding colonnade. This initial phase was completely overhauled during the reign of Emperor Hadrian, around AD…
-

Vesta: The Goddess of Hearth and Home Vesta, the revered goddess of the hearth, symbolizes the sacred fire that resides within homes, emphasizing purity and virginity. She is remembered not only through offerings of food, incense, and milk but also through the devotion of her priestesses and the cultural rituals surrounding her worship. Vesta in…
-

Understanding Ceres: The Roman Goddess of Agriculture The figure of Ceres has deep historical significance, connected to the origins of agriculture, which began approximately 10,000 years ago as the climate warmed post-Ice Age. This period marked humanity’s shift toward cultivating crops to ensure a consistent food supply, reducing reliance on hunting and foraging. This agricultural…
-

Roman Religion: An Overview of Beliefs and Practices Roman religion, encompassing the beliefs and practices of the inhabitants of the Italian peninsula from ancient times until the rise of Christianity in the 4th century CE during Classical antiquity, stands as a fascinating study of spirituality and cultural identity. According to Cicero, a notable Roman orator…
-
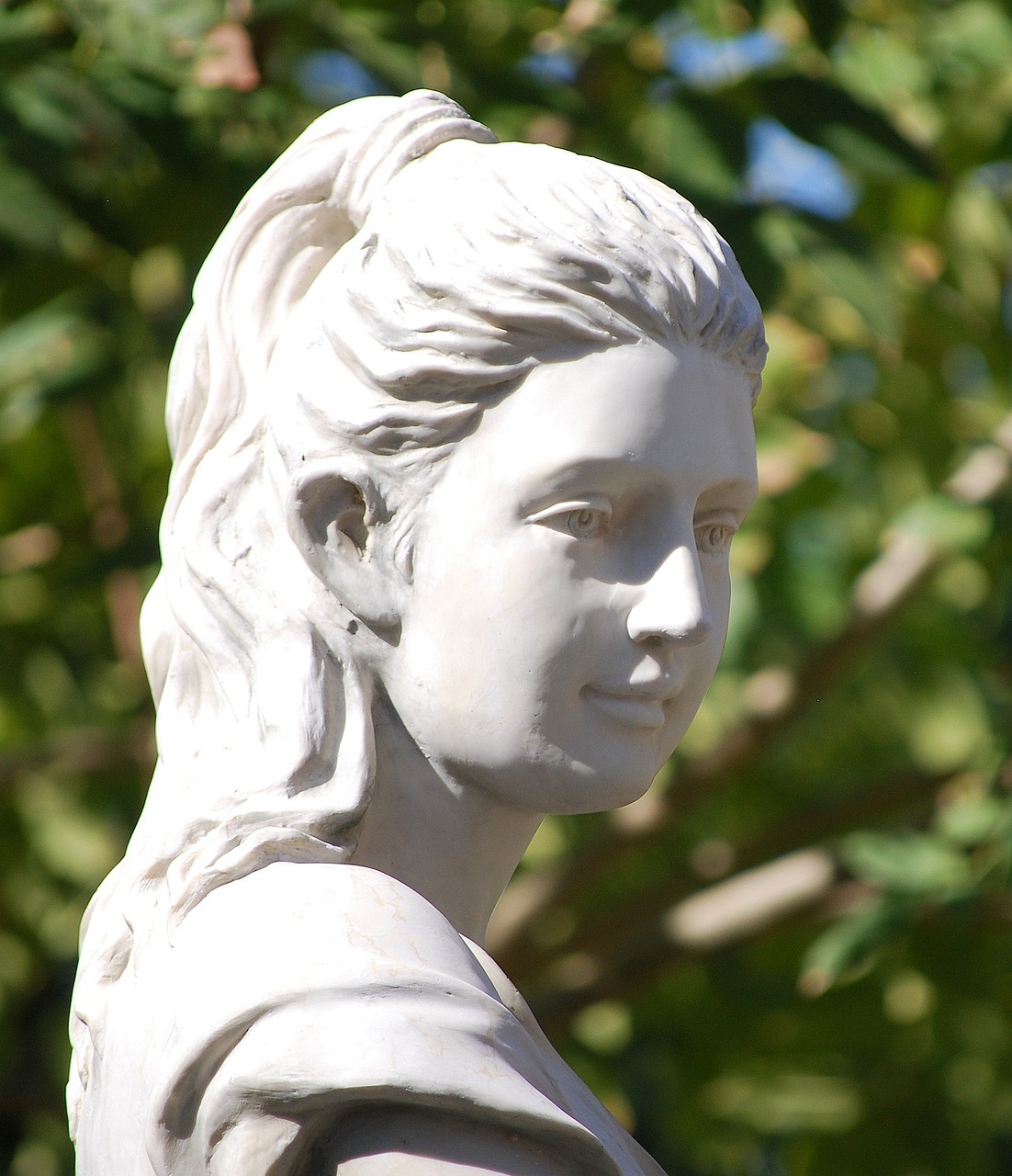

Overview of Juno in Roman Mythology Juno, also known by the Latin name Iuno, occupies a significant role as the queen of the Roman gods and the consort of Jupiter, their king. Esteemed as a protector and advocate for women, particularly in the spheres of marriage and motherhood, her mythology and visual representation were largely…
-

Ceres, the Roman goddess associated with agriculture and harvest, plays an integral role in mythology, symbolizing both bounty and scarcity. While her blessings bring about abundant crops, her discontent leads to blight and famine. She is often envisioned as a nurturing matron adorned with symbols such as the sickle, grains, and cornucopia. Her Greek equivalent…
-

Understanding Bellona: The Roman Goddess of War Polytheism in Ancient Rome Before Christianity became the Roman Empire’s official religion in the mid-4th century, Rome embraced a polytheistic belief system where numerous gods were worshipped through festivals and sacrifices year-round. Status held significant importance in this society, leading to veneration of major deities, such as Jupiter,…
-
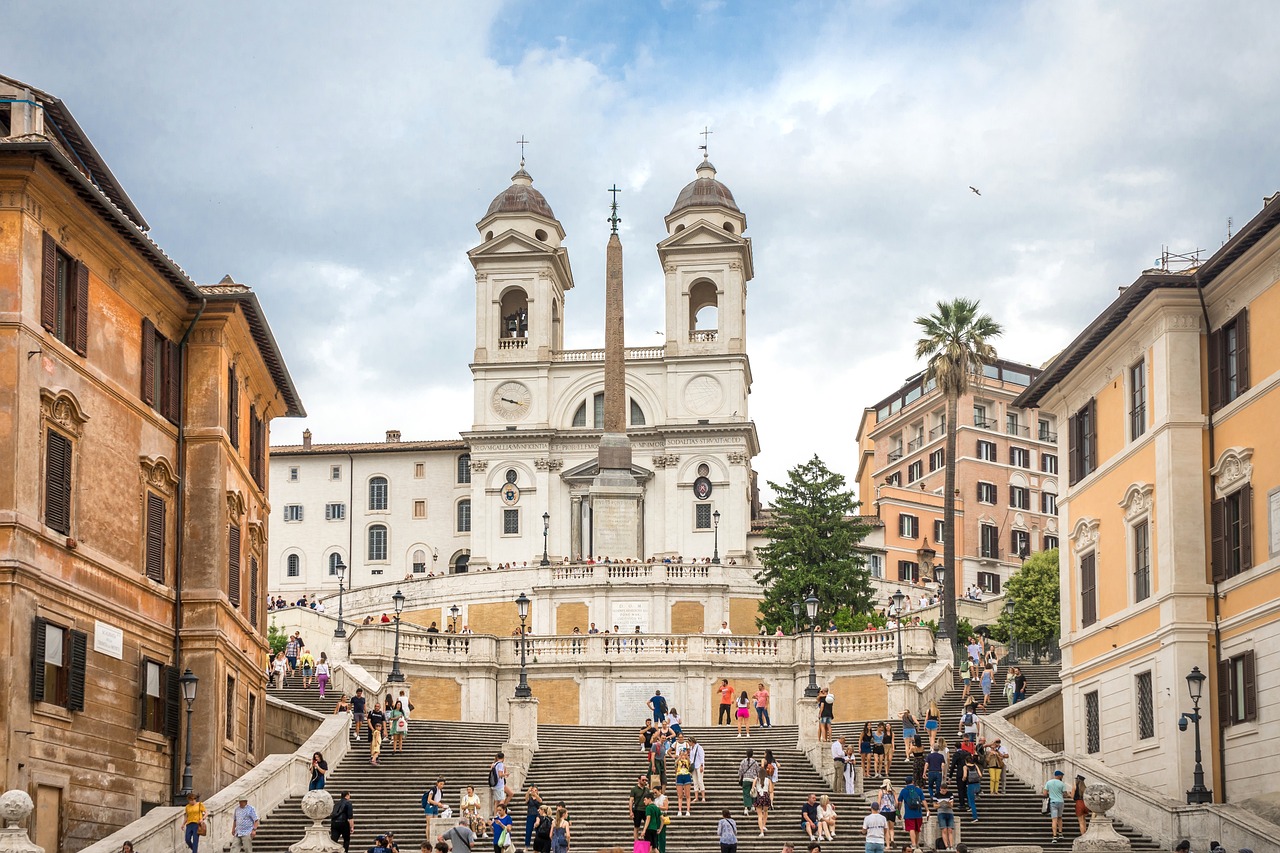

Photograph: Shutterstock Exploring the Unmissable Sights of Rome: A Traveler’s Guide The heart of the ancient Roman Empire and the center of the Papacy, Rome stands as one of the world’s most extraordinary cities. Its rich tapestry of history spans thousands of years, flaunting landmarks such as the Colosseum, Roman Forum, and the Pantheon. However,…
-

Eris: The Goddess of Discord Eris embodies the essence of strife, discord, contention, and rivalry. In ancient depictions, she is often associated with the chaos of battle, relishing in the bloodshed that war brings. Notably, her contentious spirit led to her exclusion from the wedding of Peleus and Thetis. In a fit of rage, she…
-
Neptune, the Roman deity governing the sea, shares his roots with the Greek god Poseidon. Initially revered as a god of freshwater, Neptune’s identity evolved as he adopted Poseidon’s characteristics during the integration of Greek and Roman mythologies. He inhabits an opulent palace beneath the ocean’s surface, ruling over a domain filled with sea gods…


